The Unseen Trigger: Medications and Their Impact on Acne
Related Articles: The Unseen Trigger: Medications and Their Impact on Acne
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Unseen Trigger: Medications and Their Impact on Acne. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Unseen Trigger: Medications and Their Impact on Acne
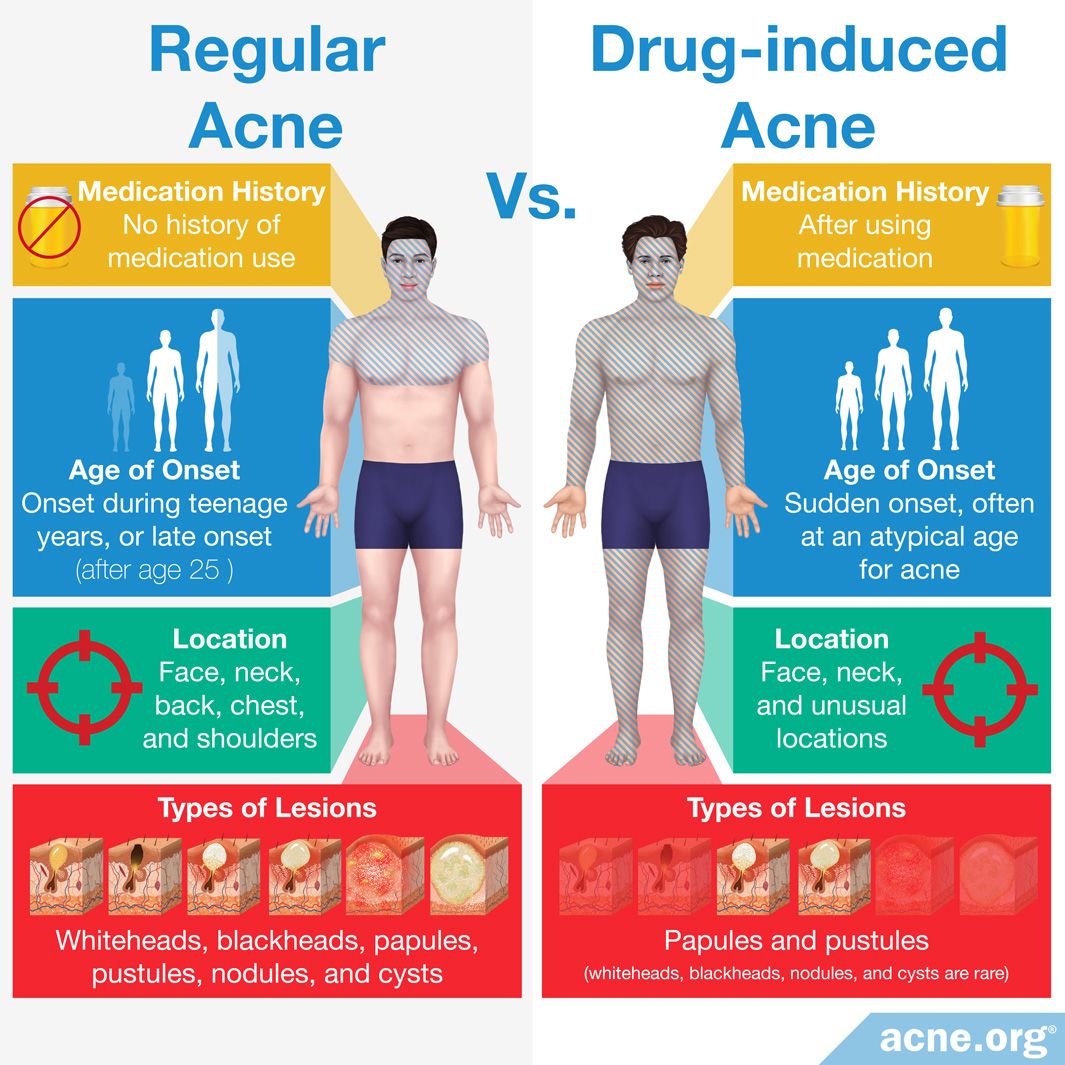
Acne, a common skin condition characterized by blemishes, pimples, and inflamed lesions, affects a significant portion of the population. While hormonal fluctuations, genetics, and environmental factors are often cited as contributing factors, less known is the potential impact of medications on acne development. This article delves into the complex relationship between various drugs and acne, providing a comprehensive overview of the mechanisms involved and offering guidance for individuals experiencing medication-induced acne.
Understanding the Link: How Medications Trigger Acne
The connection between medications and acne stems from diverse mechanisms, including:
- Hormonal Alterations: Some medications, particularly those containing hormones, can disrupt the delicate balance of hormones in the body. This disruption can lead to increased sebum production, a major contributor to acne.
- Increased Inflammation: Certain drugs can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to increased redness, swelling, and the formation of acne lesions.
- Pore Blockage: Some medications, such as lithium, can cause the skin to become thicker and more prone to pore blockage, a key factor in acne development.
- Immune System Modulation: Medications that suppress the immune system can make individuals more susceptible to bacterial infections, which can exacerbate acne.
Common Medications Associated with Acne
While numerous medications can potentially trigger acne, some are more frequently linked to this condition. These include:
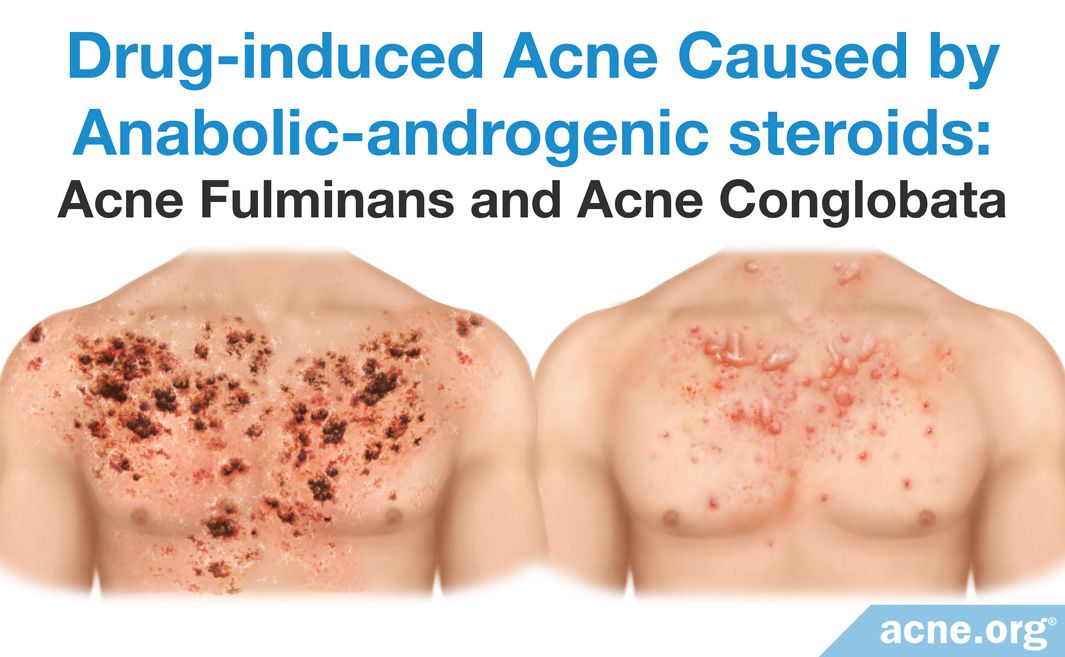
1. Androgens and Anabolic Steroids:
Androgens, including testosterone, are male sex hormones that play a role in sebum production. Medications containing androgens, such as those used for hormone replacement therapy, can lead to increased sebum production and acne. Anabolic steroids, used for building muscle mass, also contain androgens and can exacerbate acne.
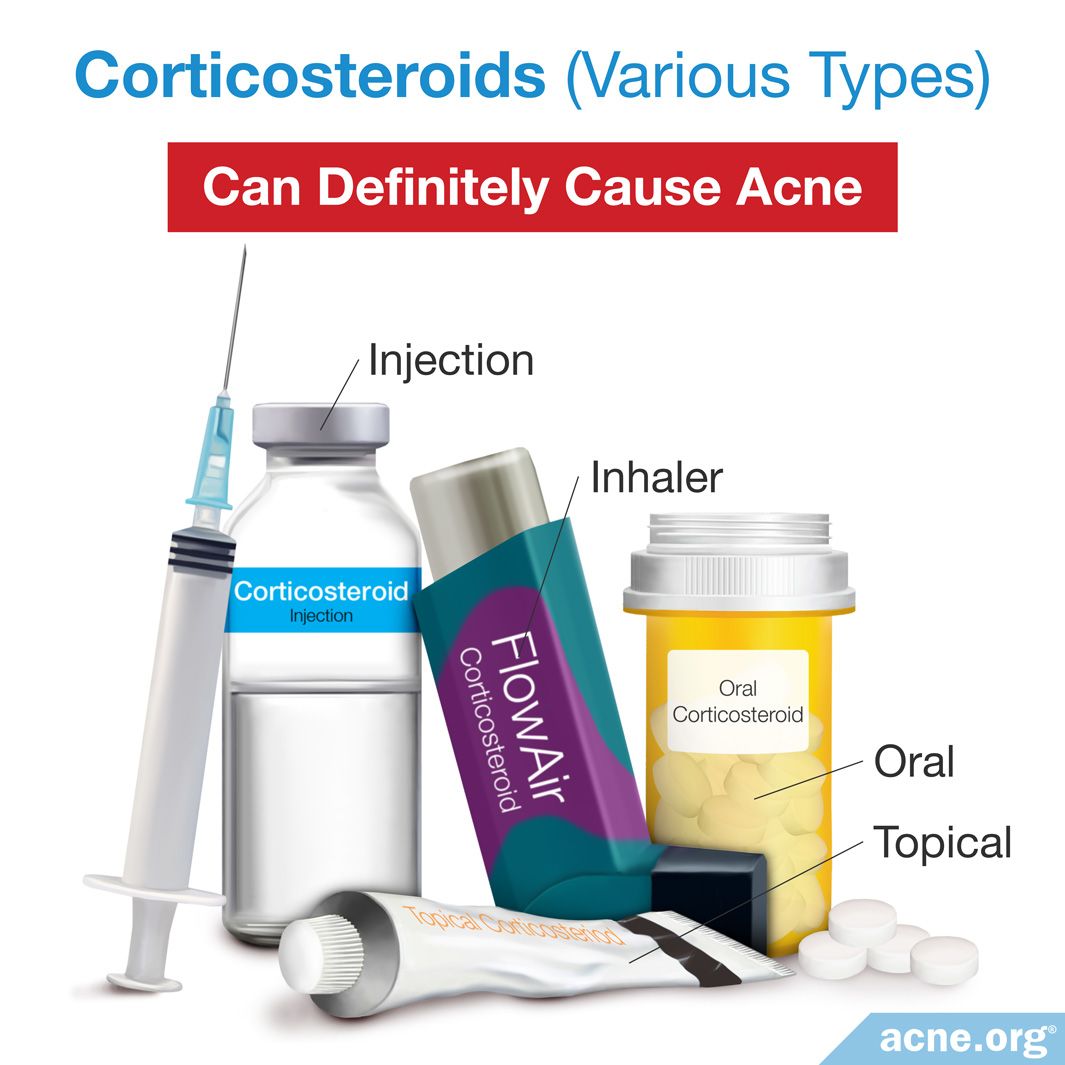
2. Corticosteroids:
Corticosteroids, often prescribed for inflammatory conditions, can have a paradoxical effect on acne. While they are known to suppress inflammation, they can also trigger an inflammatory response in the skin, leading to acne flare-ups.
3. Lithium:
Lithium, a medication used to treat bipolar disorder, can cause skin thickening and pore blockage, contributing to acne.
4. Anticonvulsants:
Certain anticonvulsants, such as valproic acid and phenytoin, are associated with acne. They can increase sebum production and inflammation, leading to breakouts.
5. Immunosuppressants:
Immunosuppressants, used to suppress the immune system in conditions like organ transplantation, can increase the risk of acne by weakening the body’s defense against bacterial infections.
6. Other Medications:
Several other medications can contribute to acne, including:
- Antibiotics: While antibiotics are generally used to treat acne, some individuals may experience breakouts as a side effect.
- Antipsychotics: Certain antipsychotics, such as olanzapine and risperidone, can cause acne as a side effect.
- Vitamin B12: High doses of Vitamin B12 can sometimes trigger acne, though this is not a common occurrence.
Navigating Medication-Induced Acne: Strategies and Solutions
If you suspect your medication is causing acne, consult your healthcare provider. They can evaluate your situation, consider alternative medications, or adjust your current regimen. Here are some strategies to manage medication-induced acne:
- Skincare Routine: Maintain a consistent skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing, exfoliation, and moisturizing.
- Over-the-Counter Products: Utilize over-the-counter acne treatments containing benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid to combat blemishes.
- Prescription Medications: If over-the-counter treatments prove ineffective, your healthcare provider may prescribe topical or oral medications, such as retinoids, antibiotics, or hormonal treatments.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy diet, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep can support overall skin health and potentially minimize acne severity.
FAQs about Medications and Acne
1. Can all medications cause acne?
No, not all medications cause acne. However, certain medications, particularly those affecting hormone levels, inflammation, or skin function, are more likely to trigger breakouts.
2. How long does it take for medication-induced acne to appear?
The time it takes for medication-induced acne to appear varies depending on the medication and individual sensitivity. Some individuals may experience breakouts within a few weeks, while others may take months to develop acne.
3. Can I stop taking my medication if it causes acne?
Never stop taking your medication without consulting your healthcare provider. Self-medicating can be dangerous and could lead to serious health complications.
4. Is medication-induced acne permanent?
Medication-induced acne is usually temporary and resolves once the medication is discontinued or the dose is adjusted. However, in some cases, the acne may persist even after stopping the medication.
5. What should I do if I suspect my medication is causing acne?
Contact your healthcare provider immediately. They can evaluate your situation and provide appropriate guidance.
Tips for Managing Medication-Induced Acne
- Communicate with your healthcare provider: Openly discuss any concerns about medication-induced acne with your doctor.
- Keep a medication log: Track your medications, dosages, and any associated skin changes to help identify potential triggers.
- Practice good hygiene: Cleanse your skin regularly with a gentle cleanser, avoid touching your face, and change pillowcases frequently.
- Protect your skin from the sun: Use sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to protect your skin from sun damage, which can worsen acne.
- Consider a dermatologist: If your acne is severe or persistent, seek professional advice from a dermatologist.
Conclusion
While medications are essential for treating various health conditions, it is crucial to be aware of their potential impact on skin health. Understanding the link between medications and acne empowers individuals to proactively address any concerns and seek appropriate guidance from healthcare professionals. By maintaining open communication with their doctors, adopting effective skincare practices, and making lifestyle modifications, individuals can minimize the impact of medication-induced acne and maintain healthy, clear skin.

.jpg.24cd6ff4644d27f1fd39ba24c4d5ae53.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/acnegrade-77453326ccf845e0bfa7105ca93f20d8.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Unseen Trigger: Medications and Their Impact on Acne. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!