The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide

Acne, a common skin condition affecting millions worldwide, is often exacerbated by external factors, including makeup. While the notion that makeup is inherently bad for acne is a simplification, understanding the nuances of this relationship is crucial for maintaining healthy skin. This article delves into the intricate interplay between makeup and acne, exploring the potential risks, benefits, and strategies for mitigating negative impacts.
The Mechanics of Acne: A Primer
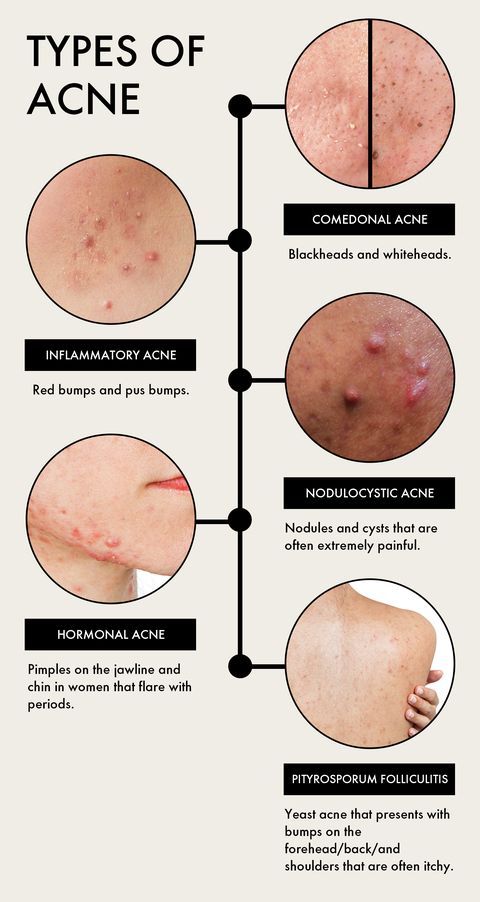
Acne arises from a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Excess Sebum Production: The skin’s natural oil, sebum, can clog pores when produced in excess.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Hormones, particularly during puberty, menstruation, or pregnancy, can stimulate sebum production.
- Bacteria: Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), a common bacteria residing on the skin, can thrive in clogged pores, leading to inflammation.
- Inflammation: The body’s immune response to P. acnes and trapped sebum can trigger redness, swelling, and pus formation.
Makeup and Acne: A Closer Look
Makeup, a ubiquitous part of many individuals’ routines, can contribute to acne in various ways:
- Clogging Pores: Certain ingredients in makeup, such as oils, waxes, and silicones, can trap sebum and dead skin cells, leading to clogged pores. This is particularly true for heavy, oil-based formulas.
- Irritating the Skin: Some makeup ingredients, like fragrances, dyes, and preservatives, can irritate sensitive skin, triggering inflammation and exacerbating existing acne.
- Promoting Bacterial Growth: Improper hygiene practices, such as sharing makeup or failing to clean brushes regularly, can introduce bacteria to the skin, contributing to acne breakouts.
The Role of Makeup Ingredients
Not all makeup is created equal. Some ingredients are more likely to contribute to acne than others. Key culprits include:
- Comedogenic Ingredients: These ingredients are known to clog pores, such as coconut oil, lanolin, and cocoa butter.
- Occlusive Ingredients: These ingredients form a barrier on the skin, trapping moisture and potentially exacerbating acne, including mineral oil, petrolatum, and dimethicone.
- Fragrances and Dyes: These synthetic ingredients can irritate sensitive skin and trigger inflammation.
- Alcohol: While often used as a drying agent, alcohol can strip the skin’s natural oils, leading to increased sebum production and potential irritation.
Navigating the Makeup Landscape: Choosing Acne-Friendly Options
Despite the potential risks, makeup can be enjoyed even with acne-prone skin. Here are some key considerations:
- Choose Non-Comedogenic Products: Opt for makeup labeled "non-comedogenic" or "oil-free," as these are less likely to clog pores.
- Prioritize Water-Based Formulas: Water-based formulas tend to be lighter and less likely to trap sebum, making them suitable for acne-prone skin.
- Look for Ingredients That Benefit Acne: Some ingredients can actually help manage acne, such as salicylic acid, tea tree oil, and niacinamide.
- Pay Attention to Packaging: Avoid products with pumps or applicators that can harbor bacteria.
- Clean Brushes Regularly: Regularly cleaning makeup brushes and sponges with a gentle cleanser helps prevent bacterial buildup.
Beyond Ingredients: Makeup Application and Hygiene
Proper application techniques and hygiene practices play a crucial role in minimizing the impact of makeup on acne:
- Cleanse Thoroughly: Before applying makeup, cleanse the skin thoroughly with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt, oil, and bacteria.
- Apply Sparingly: Use a light hand when applying makeup, particularly on areas prone to breakouts.
- Remove Makeup Completely: Remove all makeup before bed, as leaving it on overnight can clog pores and promote bacterial growth.
- Avoid Touching Your Face: Frequent touching can transfer bacteria and oil to the skin, exacerbating acne.
The Potential Benefits of Makeup
While makeup can be a potential acne trigger, it can also offer benefits for individuals with acne:
- Concealing Imperfections: Makeup can help camouflage blemishes and redness, boosting confidence and improving self-esteem.
- Protecting the Skin: Some makeup products contain SPF, which can protect the skin from harmful UV rays, a factor that can exacerbate acne.
- Creating a Barrier: Certain makeup ingredients can form a protective barrier on the skin, reducing irritation and inflammation.
FAQs Regarding Makeup and Acne
Q: Is it okay to wear makeup if I have acne?
A: Wearing makeup is generally safe for individuals with acne, provided they choose the right products and practice good hygiene.
Q: What are the best makeup brands for acne-prone skin?
A: Several brands cater to acne-prone skin, including:
- CeraVe: Known for its gentle, non-comedogenic formulas.
- La Roche-Posay: Offers a range of products with ingredients like salicylic acid and niacinamide.
- Clinique: Known for its allergy-tested and fragrance-free products.
- bareMinerals: Focuses on mineral-based makeup, often considered gentle on sensitive skin.
Q: Can makeup worsen existing acne?
A: Yes, certain makeup ingredients and application practices can worsen existing acne. However, choosing the right products and following proper hygiene can mitigate these risks.
Q: Should I avoid foundation if I have acne?
A: Not necessarily. Look for oil-free, non-comedogenic foundations specifically designed for acne-prone skin.
Q: How often should I clean my makeup brushes?
A: It is recommended to clean makeup brushes and sponges at least once a week to prevent bacterial buildup.
Q: What are some tips for applying makeup with acne?
A:
- Apply makeup with clean hands and brushes.
- Use a light touch, particularly on acne-prone areas.
- Blend products well to avoid a cakey look.
- Avoid using harsh scrubs or exfoliating products on active breakouts.
- Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice.
Conclusion
The relationship between makeup and acne is complex and multifaceted. While certain makeup ingredients and application practices can contribute to acne, choosing the right products and following proper hygiene can mitigate these risks. Makeup can also offer benefits for individuals with acne, including concealing imperfections and protecting the skin. By understanding the nuances of this relationship and adopting a proactive approach, individuals with acne can enjoy the benefits of makeup while maintaining healthy skin.
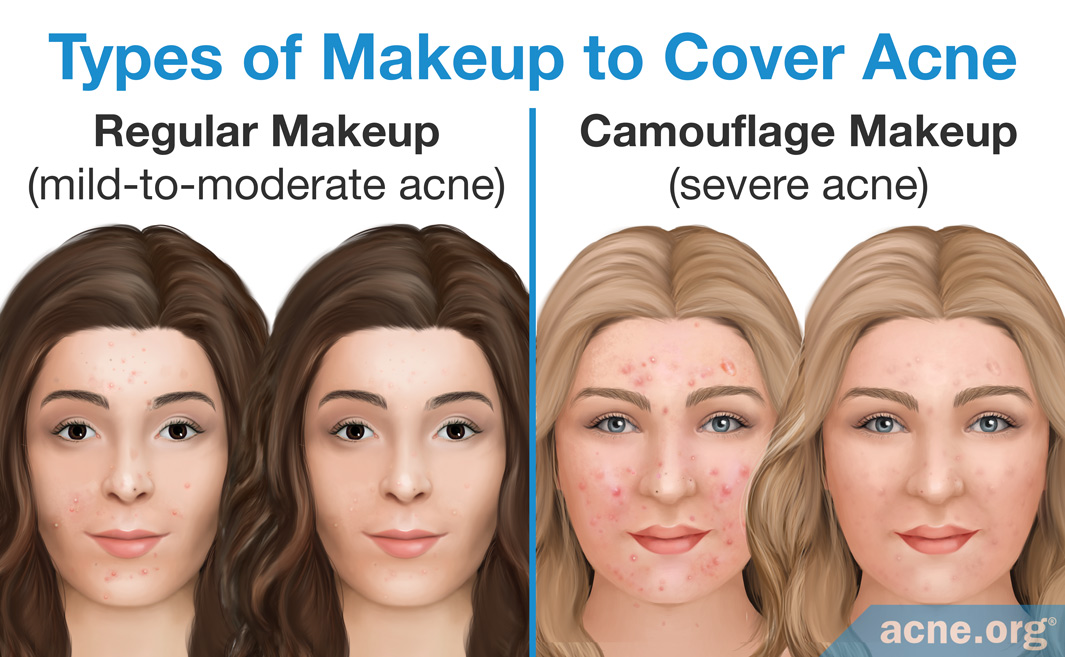






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Complex Relationship Between Makeup and Acne: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!